React:
A Front-End
Framework
Objectives
-
Define front-end frameworks
-
Describe React at a high level
Front-End Frameworks
JavaScript libraries that handle DOM manipulation
Handles navigations (HTML5 push state)
State management
Single Page Apps
Front-End Framework
GET /
index.html
GET /bundle.js
bundle.js (includes JS for framework)
Framework is in control of the DOM
Node.js
React
React
-
Release by Facebook in 2013
-
A view library that uses composable components
-
Other libraries are commonly used with React


Redux
React Router
Composable Components
LIVE
CODE
First React Component
JSX
Objectives
-
Define babel, a transpiler
-
Use JSX in our react component
JSX
With
JavaScript
Objectives
-
Write JavaScript inside JSX
-
Use a style attribute in JSX
-
Add a className attribute
Multiple
Components
Objectives
-
Render an array of JSX
-
Use a React component inside of another component

Transpiler: converts from one source code version to another
JSX
Vanilla JS
Create
React
App
Objectives
-
Describe Webpack
-
Install Create React App
-
Make an application using Create React App
Webpack

-
Combines different JS files into a bundle.js
-
Has a plugin system to run tools like babel
-
Also bundles other assets like css, images, etc
A module bundler for modern JavaScript applications
Create React App Uses Webpack

Priorities
-
Learn React
-
Learn to configure Webpack
Create React App:
Files
JavaScript
Import
Statement
Objectives
-
Import a component from another file
-
Export a component from a file
-
Use export default vs non default export
MDN Import
React
Props
Objectives
-
Define props
-
Use props inside of a component
Props
Immutable data passed to your components
class ShowText extends Component {
render() {
// Inside the render method, we have
// access to this.props (this refers
// to the ShowText instance).
return <div>{this.props.text}</div>;
}
}Accessible in your component as an object called: this.props
Passing In Props
To A Component
<ShowText
text="This is a prop named text"
/>class ShowText extends Component {
render() {
return <div>{this.props.text}</div>;
}
}Props Are Immutable
class ShowText extends Component {
render() {
// Never ever change this.props
this.props.text = "WRONG!!"; // Causes a TypeError
this.props = {}; // Never do this!!
this.props.newProp = "Also wrong"; // Use default props
return <div>{this.props.text}</div>;
}
}
Recipe App
With Props
Recipe App
With Props
(Continued)
Objectives
-
Use props in an application
defaultProps
propTypes
Objectives
-
Use defaultProps to give props a default value
-
Use propTypes to specify what props a component is expecting
defaultProps
Default values for props in a component
class IngredientList extends Component {
static defaultProps = {
ingredients: []
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.ingredients.map((ing, index) => (
<li key={index}>{ing}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}defaultProps
This syntax also works
class IngredientList extends Component {
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.ingredients.map((ing, index) => (
<li key={index}>{ing}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}
IngredientList.defaultProps = {
ingredients: []
};class App extends Component {
static defaultProps = {
recipes: [{
title: "Spaghetti",
ingredients: ["flour", "water"],
instructions: "Mix ingredients",
img: "spaghetti.jpg"
}]
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.props.recipes.map((r, index) => (
<Recipe key={index} title={r.title}
ingredients={r.ingredients}
img={r.img} instructions={r.instructions}
/>
))}
</div>
);
}
}class App extends Component {
static defaultProps = {
recipes: [{
title: "Spaghetti",
ingredients: ["flour", "water"],
instructions: "Mix ingredients",
img: "spaghetti.jpg"
}]
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.props.recipes.map((r, index) => (
<Recipe key={index} {...r} />
))}
</div>
);
}
}PropTypes
Development time type checker for your props
Installation:
npm install --save prop-types
PropTypes
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class IngredientList extends Component {
static propTypes = {
ingredients: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.string)
.isRequired
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.ingredients.map((ing, index) => (
<li key={index}>{ing}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}Facebook PropTypes Docs
Recipe App
With Props
(Exercise)
Recipe App
With Props
(Solution)
props.children
Objectives
-
Describe what props.children does
-
Read more about props.children helper methods
props.children
A collection of the children inside of a component...
Let's see an example
Row Example
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Row>
<p>Timothy</p>
<div>Moxie</div>
<h1>React</h1>
</Row>
);
}
}Row Example
class Row extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{
display: 'flex',
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-around',
}}>
{this.props.children}
</div>
)
}
}Row Rendered
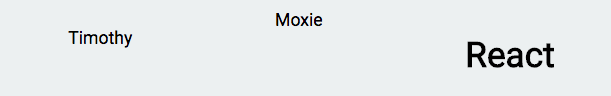
Read More
Intro to
State
Objectives
-
Define state in React
-
Create a component with a constructor and state
-
Describe what happens when setState is called
State
Stateful data
Data in our application that can change
State Example
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { favColor: 'red' };
}
render() {
return (
<div>
My favorite color:
{this.state.favColor}
</div>
);
}
}setState
The correct way to change state in your application
this.setState({ });Simplest Usage: setState accepts an object with new properties and values for this.state
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { favColor: 'red' };
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({favColor: 'blue'})
}, 3000);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
My favorite color:
{this.state.favColor}
</div>
);
}
}Pure
Functions
Objectives
-
Define a pure function
Pure Function
A function with no side effects
It does not modify its inputs
It's repeatable
(same inputs, same outputs)
Not A Pure Function
function doubleVals(arr) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] * 2;
}
return arr;
}Pure Function
function doubleVals(arr) {
return arr.map(v => v * 2);
}Not A Pure Function
var person = {id: 53, name: "Tim"};
function addJob(job){
person.job = job;
}
addJob("Instructor");
Pure Function
var person = {id: 53, name: "Tim"};
function addJob(personObj, job){
return Object.assign({},
perosnObj,
{job});
}
addJob(person, "Instructor");
Object Spread
var person = {id: 53, name: "Tim"};
function addJob(personObj, job){
return {...personObj, job};
}
addJob(person, "Instructor");
What does this have to do with React?
All changes to this.state
should be pure