React:
A Front-End
Framework
Objectives
-
Define front-end frameworks
-
Describe React at a high level
Front-End Frameworks
JavaScript libraries that handle DOM manipulation
Handles navigations (HTML5 push state)
State management
Single Page Apps
Front-End Framework
GET /
index.html
GET /bundle.js
bundle.js (includes JS for framework)
Framework is in control of the DOM
Node.js
React
React
-
Release by Facebook in 2013
-
A view library that uses composable components
-
Other libraries are commonly used with React


Redux
React Router
Composable Components
LIVE
CODE
First React Component
JSX
Objectives
-
Define babel, a transpiler
-
Use JSX in our react component
JSX
With
JavaScript
Objectives
-
Write JavaScript inside JSX
-
Use a style attribute in JSX
-
Add a className attribute
Multiple
Components
Objectives
-
Render an array of JSX
-
Use a React component inside of another component

Transpiler: converts from one source code version to another
JSX
Vanilla JS
Create
React
App
Objectives
-
Describe Webpack
-
Install Create React App
-
Make an application using Create React App
Webpack

-
Combines different JS files into a bundle.js
-
Has a plugin system to run tools like babel
-
Also bundles other assets like css, images, etc
A module bundler for modern JavaScript applications
Create React App Uses Webpack

Priorities
-
Learn React
-
Learn to configure Webpack
Create React App:
Files
JavaScript
Import
Statement
Objectives
-
Import a component from another file
-
Export a component from a file
-
Use export default vs non default export
MDN Import
React
Props
Objectives
-
Define props
-
Use props inside of a component
Props
Immutable data passed to your components
class ShowText extends Component {
render() {
// Inside the render method, we have
// access to this.props (this refers
// to the ShowText instance).
return <div>{this.props.text}</div>;
}
}Accessible in your component as an object called: this.props
Passing In Props
To A Component
<ShowText
text="This is a prop named text"
/>class ShowText extends Component {
render() {
return <div>{this.props.text}</div>;
}
}Props Are Immutable
class ShowText extends Component {
render() {
// Never ever change this.props
this.props.text = "WRONG!!"; // Causes a TypeError
this.props = {}; // Never do this!!
this.props.newProp = "Also wrong"; // Use default props
return <div>{this.props.text}</div>;
}
}
Recipe App
With Props
Recipe App
With Props
(Continued)
Objectives
-
Use props in an application
defaultProps
propTypes
Objectives
-
Use defaultProps to give props a default value
-
Use propTypes to specify what props a component is expecting
defaultProps
Default values for props in a component
class IngredientList extends Component {
static defaultProps = {
ingredients: []
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.ingredients.map((ing, index) => (
<li key={index}>{ing}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}defaultProps
This syntax also works
class IngredientList extends Component {
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.ingredients.map((ing, index) => (
<li key={index}>{ing}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}
IngredientList.defaultProps = {
ingredients: []
};class App extends Component {
static defaultProps = {
recipes: [{
title: "Spaghetti",
ingredients: ["flour", "water"],
instructions: "Mix ingredients",
img: "spaghetti.jpg"
}]
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.props.recipes.map((r, index) => (
<Recipe key={index} title={r.title}
ingredients={r.ingredients}
img={r.img} instructions={r.instructions}
/>
))}
</div>
);
}
}class App extends Component {
static defaultProps = {
recipes: [{
title: "Spaghetti",
ingredients: ["flour", "water"],
instructions: "Mix ingredients",
img: "spaghetti.jpg"
}]
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.props.recipes.map((r, index) => (
<Recipe key={index} {...r} />
))}
</div>
);
}
}PropTypes
Development time type checker for your props
Installation:
npm install --save prop-types
PropTypes
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class IngredientList extends Component {
static propTypes = {
ingredients: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.string)
.isRequired
}
render() {
return (
<ul>
{this.props.ingredients.map((ing, index) => (
<li key={index}>{ing}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
}Facebook PropTypes Docs
Recipe App
With Props
(Exercise)
Recipe App
With Props
(Solution)
props.children
Objectives
-
Describe what props.children does
-
Read more about props.children helper methods
props.children
A collection of the children inside of a component...
Let's see an example
Row Example
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Row>
<p>Timothy</p>
<div>Moxie</div>
<h1>React</h1>
</Row>
);
}
}Row Example
class Row extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{
display: 'flex',
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-around',
}}>
{this.props.children}
</div>
)
}
}Row Rendered
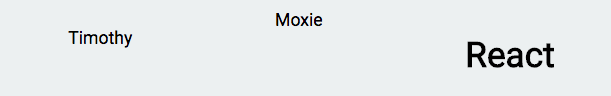
Read More
Intro to
State
Objectives
-
Define state in React
-
Create a component with a constructor and state
-
Describe what happens when setState is called
State
Stateful data
Data in our application that can change
State Example
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { favColor: 'red' };
}
render() {
return (
<div>
My favorite color:
{this.state.favColor}
</div>
);
}
}setState
The correct way to change state in your application
this.setState({ });Simplest Usage: setState accepts an object with new properties and values for this.state
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { favColor: 'red' };
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({favColor: 'blue'})
}, 3000);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
My favorite color:
{this.state.favColor}
</div>
);
}
}Pure
Functions
Objectives
-
Define a pure function
Pure Function
A function with no side effects
It does not modify its inputs
It's repeatable
(same inputs, same outputs)
Not A Pure Function
function doubleVals(arr) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] * 2;
}
return arr;
}Pure Function
function doubleVals(arr) {
return arr.map(v => v * 2);
}Not A Pure Function
var person = {id: 53, name: "Tim"};
function addJob(job){
person.job = job;
}
addJob("Instructor");
Pure Function
var person = {id: 53, name: "Tim"};
function addJob(personObj, job){
return Object.assign({},
perosnObj,
{job});
}
addJob(person, "Instructor");
Object Spread
var person = {id: 53, name: "Tim"};
function addJob(personObj, job){
return {...personObj, job};
}
addJob(person, "Instructor");
What does this have to do with React?
All changes to this.state
should be pure
Update Complex
State Exercise
Update Complex
State Solution
Lots of Stuff Early React
By Elie Schoppik
Lots of Stuff Early React
- 2,261



